Risk management is a crucial part of project management. Imagine you're about to embark on an exciting adventure, like climbing a mountain. You wouldn't start the climb without identifying problems that might occur and ways to overcome them. Things like packing the right gear, checking the weather, and ensuring you have a plan for emergencies. Being prepared for contingencies is essentially what risk management is all about - in life and in projects.
Why Risk Management is Important
First off, why should you care about risk management? Well, every project has its share of uncertainties and potential problems. These are called risks. They can affect your project’s schedule, cost, and overall success.
By managing risks, you can minimize the chances of things going wrong and increase the chances of completing your project successfully.
What Project Managers Need to Do to Manage Risk
To manage risk, project managers should follow these steps:
Identify Risks Early: In conjunction with your team, start by making a list of all the things that could possibly go wrong. This can include anything from running out of money to having a key team member leave the project. Getting input from your customer stakeholders is worth the effort as well. This widens the view and allows the project to touch as many facets of risk as possible.
Analyze Risks: Once you've identified the risks, you need to figure out which ones are the most serious. Think about how likely each risk is to happen and what the impact would be if it did.
Plan Risk Response Strategies: For each risk, decide what you’re going to do about it. There are four main strategies: Avoiding the risk, reducing the risk, transferring the risk to someone else, or accepting the risk.
Monitor and Control - Review: Keep an eye on your risks throughout the project. Some risks might become more or less significant as things progress, so be ready to adjust your plans as needed.
How to Quantify Risk
Quantifying risk means figuring out how serious each risk is. This usually involves two qualitative factors:
Likelihood: How likely is it that the risk will happen?
Impact: If the risk does happen, how bad will it be for the project?
You can use a simple scale for both factors, such as 1 (low) to 5 (high). Multiply the likelihood and impact scores together to get a risk score. For example, a risk with a likelihood of 4 and an impact of 3 would have a risk score of 12.
Here’s an example using a 3 by 3 grid:
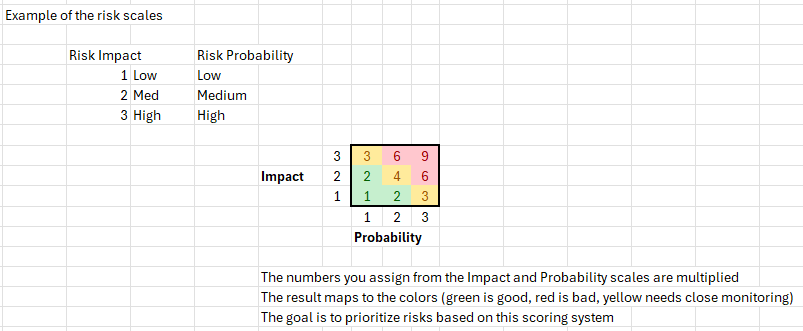
How to Budget a Risk Reserve
A risk reserve is like an emergency fund; a contingency fund set aside to cover potential risks if they occur. To budget for a risk reserve:
Estimate Costs: For each risk on your list, estimate the cost if that risk happens. This could include things like additional materials, overtime pay, rework, or consultant fees. Also determine its likelihood.
Calculate Total: Add up the estimated costs of all the risks. This gives you the total amount of money you might need to handle all identified risks.
Set Aside Funds: Based on the total calculated, decide how much money to set aside as your risk reserve. You may not be able to budget enough to cover all risks, so you’ll need to determine where to draw the line and accept some risks with the lowest impact.

How to Decide Which Risks Need to Be Mitigated and Which Can Be Ignored
Mitigation means taking steps to reduce the impact or likelihood of a risk. Here’s how to decide what to mitigate and what to ignore:
Risk Score: Use the risk scores you calculated to prioritize risks. Focus on risks with the highest scores first, as they are the most serious.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Consider whether the cost of mitigating a risk is worth the benefit. If mitigating a risk is very expensive but the impact of the risk is relatively small, it might be better to accept the risk.
Acceptable Risks: Some risks are acceptable. If the likelihood and impact are both low, you might decide that it’s not worth spending time or money on mitigation.
Critical Risks: Any risks that have a high impact on the project’s success should definitely be mitigated. These are the risks that could cause major delays or cost overruns.
Conclusion
Risk management might seem complicated at first, but it’s all about being prepared. You need to plan for what could go wrong, have strategies in place, and keep an eye on things as you go. Regular risk reviews with your team and stakeholders is best practice and raises awareness for all parties. The goal is not to eliminate all risks, rather manage them in a way that minimizes their impact. By managing risks effectively, you can help ensure that your projects run smoothly and successfully.
Please share this if you found it useful

Your to-do list:
⏩If you're interested in the Project Management career field, DM me with questions on LinkedIn.
P.S. Embark on your project management journey today. "Inside the Project Manager's World" is your passport to a dynamic career path, providing insights, answers, and skills to propel you toward project management excellence.
P.P.S Like fun stuff?
👉 Celebrate your Project Management career with wearables and useful items here on TeePublic
P.P.P.S. (it’s a thing)
If you're interested in starting a newsletter like mine, try beehiiv (it's what I use)
